Health
Traditional family planning methods have 50% failure rate, says DEVCOMS

By Francesca Hnageior.
Traditional family planning methods have 50% failure rate, says DEVCOMS
A media development organisation, Development Communications Network, has encouraged women of reproductive age to embrace modern contraceptive methods of family planning to prevent unplanned pregnancies.
DEVCOMS noted that the traditional methods of family planning including periodic abstinence, withdrawal, and lactational amenorrhea were unreliable.
It disclosed that traditional family methods have a high failure rate of more than 50 per cent.
The Program Director of DEVCOMS, Akin Jimoh, stated this on Thursday during a courtesy visit to The Punch Place, the headquarters of Punch Nigeria Limited.
Jimoh said, “When you look at traditional methods of family planning, the failure rate is high—sometimes more than 50 percent.
“However, there are several modern methods available that suit an individual’s body system. You are guided through processes that will enhance your opportunities to benefit as an individual, whether you are a housewife, a woman, or a social worker.
“Additionally, there is medical support available in case of any complications. People are monitored, advised, and counseled.”
Health
‘Blessed’: US Woman Sees Second Chance In Life After Pig Kidney Transplant
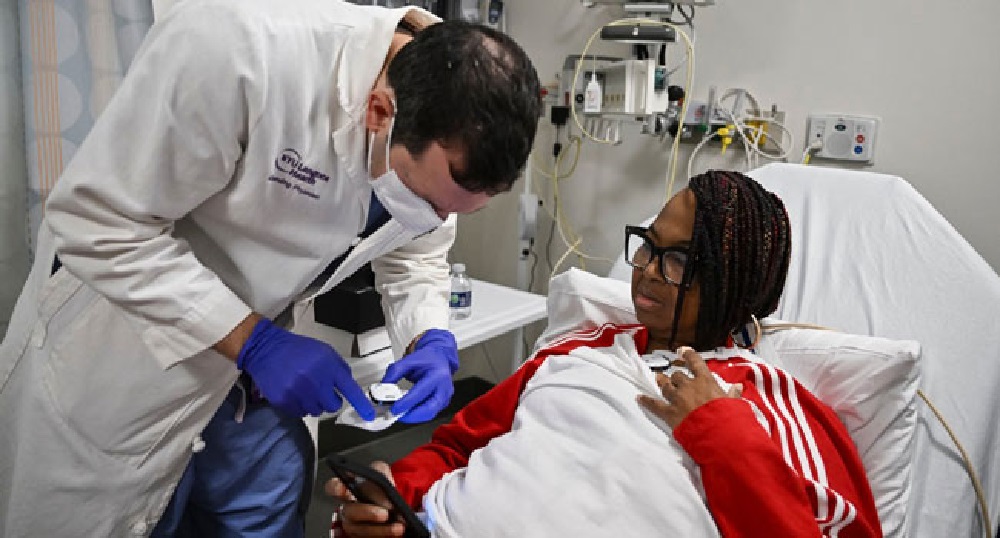
Towana Looney donated a kidney to her mother in 1999 only for the remaining one to fail years later due to pregnancy complications.
Now, the 53-year-old from Alabama has become the latest recipient of a gene-edited pig kidney — and is currently the only living person in the world with an animal organ transplant, New York’s NYU Langone hospital announced Tuesday.
“I’m overjoyed, I’m blessed to have received this gift, this second chance at life,” Looney said during a press conference, held three weeks after the procedure.
Xenotransplantation, transplanting organs from one species to another, has long been a tantalizing yet elusive scientific goal. Early experiments on primates faltered, but recent advances in gene editing and immune system management have brought the dream closer to reality.
Pigs have emerged as the ideal donors: they grow quickly, produce large litters and are already part of the human food supply.
Advocates hope this approach can help address the severe organ shortage in the United States, where more than 100,000 people are waiting for transplants, including over 90,000 in need of kidneys.
A last chance
Looney had been living with dialysis since December 2016 — eight grueling years. High blood pressure caused by preeclampsia had taken its toll, leaving her with chronic kidney disease.
Despite receiving priority on transplant waiting lists as a living donor, her search for a compatible kidney was a frustrating dead end. Her unusually high levels of harmful antibodies made rejection almost inevitable, and as her body lost viable blood vessels to support dialysis, her health declined.
Out of options, Looney applied to join a clinical trial for pig kidney transplants, and finally underwent the seven-hour surgery on November 25.
Asked how she felt afterward, Looney’s joy was infectious. “I’m full of energy, I’ve got an appetite… and of course, I can go to the bathroom. I haven’t been going in eight years!” she laughed, adding that she plans to celebrate at Disney World.
Jayme Locke, a surgeon on the transplant team, described the results with awe. “The kidney functioned essentially exactly like a kidney from a living donor,” she said, adding that Looney’s husband saw a rosiness in her cheeks for the first time in years.
“That is the miracle of transplantation.”
Cautious optimism
Looney’s surgery is the third time a gene-edited pig kidney has been transplanted into a human who is not brain dead.
Rick Slayman, the first recipient, died in May, two months after his procedure at Massachusetts General Hospital. The second, Lisa Pisano, initially showed signs of recovery following her surgery at NYU Langone, but the organ had to be removed after 47 days, and she passed away in July.
Looney, however, was not terminally ill before the transplant, noted Robert Montgomery, who led the surgery. Each case, he emphasized, provides critical lessons for refining the techniques.
The kidney was provided by biotech company Revivicor, which breeds genetically modified herds in Virginia. A Massachusetts-based company, eGenesis, provided the kidney for Slayman.
Looney’s organ has 10 genetic edits to improve compatibility with the human body — an advance over Revivicor’s earlier efforts that used kidneys with a single gene edit and included the pig’s thymus gland to help train the host’s immune system and prevent rejection.
Montgomery, a pioneer in the field who performed the world’s first gene-edited pig organ transplant in a brain-dead patient in 2021, said both methods are likely to enter clinical trials “probably by this time next year, or even sooner.”
“This is a watershed moment for the future of transplantation,” said Kevin Longino, CEO of the National Kidney Foundation. The nonprofit’s polling shows that patients and families favor faster clinical trial progress, believing the risk of inaction outweighs the uncertainties of xenotransplantation.
Looney was discharged December 6 to a nearby New York City apartment. Though her high antibody levels remain a concern, doctors are monitoring her closely using wearable technology and are trying a novel drug regimen to prevent rejection.
Periodic hospital visits may still be required, but the team remains optimistic she can return home in three months.
AFP
Health
New York Doctor Sued For Mailing Abortion Pills To Texas Woman

The Republican attorney general of Texas has filed a lawsuit against a New York doctor who mailed abortion pills to a woman in the southern state.
Texas has some of the toughest laws restricting abortion in the country, and the case pits state laws regulating the procedure against each other.
Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton filed the civil suit on Thursday against Margaret Carpenter, the New York-based founder of the Abortion Coalition for Telemedicine.
The attorney general’s office said Carpenter provided a 20-year-old Texas woman with “abortion-inducing drugs that ended the life of an unborn child and resulted in serious complications for the mother.”
“Texas laws prohibit a physician or medical supplier from providing any abortion-inducing drugs by courier, delivery, or mail service,” it said.
In addition, “no physician may treat patients or prescribe Texas residents medicine through telehealth services unless the doctor holds a valid Texas medical license.”
Carpenter is not a licensed physician in Texas.
Texas is seeking an injunction against Carpenter barring her from illegally practicing medicine in the state and from prescribing abortion pills to Texas residents.
He is also seeking a $100,000 fine for each violation.
“In Texas, we treasure the health and lives of mothers and babies, and this is why out-of-state doctors may not illegally and dangerously prescribe abortion-inducing drugs to Texas residents,” Paxton said.
Democratic-controlled New York has passed a so-called shield law which provides legal protection to New York doctors who send abortion pills to women in states where the procedure has been outlawed.
Eighteen Democratic-ruled states have enacted shield laws since the US Supreme Court struck down the nationwide right to abortion in 2022, according to the Center for Reproductive Rights.
In June of this year, the top court rejected a bid by anti-abortion groups to restrict mifepristone, the pill widely used to terminate pregnancies in the United States.
The Texas lawsuit raises thorny legal questions for the courts about what is known as extraterritoriality, the application of one state’s laws to another.
AFP
Health
Malaria Vaccine Receives High S ores In Latest Treatment Evaluation Study
Malaria Vaccine Receives High Marks In Latest Treatment Evaluation StudyThe R21 malaria vaccine has been prequalified by the World Health Organization (WHO), offering an affordable and promising solution for malaria control in Africa, according to a recent study published by 1Day Africa, a global non-profit organization. The study emphasizes that the vaccine’s cost-effectiveness is comparable to that of insecticide-treated bed nets, which have long been a cornerstone in malaria prevention.
The report reveals that the R21 vaccine costs $39 per disability-adjusted life year (DALY) averted, closely rivaling the $38 cost of bed nets. In contrast, the RTS malaria vaccine costs $129 per DALY, making R21 a more cost-efficient option for large-scale distribution in low- and middle-income countries.
Produced by the Serum Institute of India, the R21 vaccine benefits from streamlined manufacturing processes, which contribute to its reduced cost. Researchers suggest that combining R21 with other malaria control measures, such as seasonal chemoprevention and vector control programs, could significantly reduce malaria cases in Sub-Saharan Africa, where the majority of global malaria incidents occur.
Malaria remains a significant public health challenge, with 95% of the world’s cases reported in Sub-Saharan Africa in 2022. The introduction of the R21 vaccine, according to the study, could reshape malaria control efforts, especially in regions facing rising resistance to traditional prevention methods.
The report calls for continued investment in malaria research and the integration of new interventions like R21 into comprehensive public health strategies to tackle the disease more effectively.
-

 Sports24 hours ago
Sports24 hours agoHumility, focus fetched my son CAF Player of the Year award – Lookman’s dad
-

 News24 hours ago
News24 hours agoFG endorses N30 billion for 30 Fed Universities of Agric to begin mechanized farming
-

 Sports14 hours ago
Sports14 hours agoCAF Awards 2024: Full List of Winners
-

 News19 hours ago
News19 hours agoInsecurity : Nigerians spent N2.2trn as payment for ransom in one year -NBS
-

 News8 hours ago
News8 hours agoGov Adeleke Speaks On Death Sentence For Chicken Thief
-

 News13 hours ago
News13 hours agoCAC deregistered 300,000 dormant companies in one year
-

 News8 hours ago
News8 hours agoJust in: CBN Imposes N100k Bar on PoS, Issues Warning to Operators
-

 News14 hours ago
News14 hours agoThree to die by hanging for killing Delta monarch








