News
HEALTH Alert! Babies in Nigeria are being born with antibiotic resistant bacteria – Study
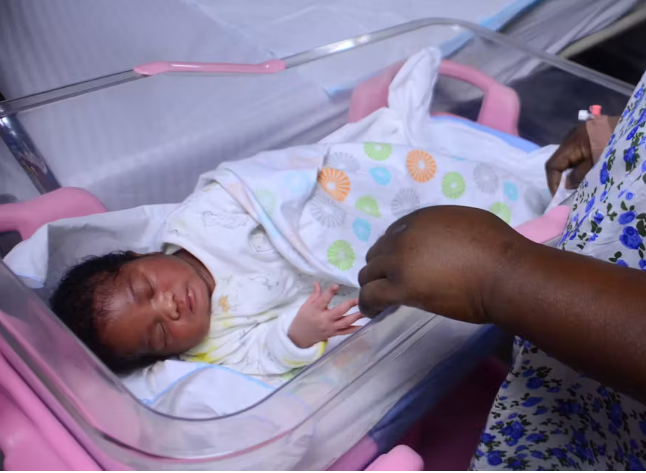
By Kayode Sanni Arewa
Sepsis occurs when one’s immune system has an extreme response to an infection. It’s a life-threatening condition: globally, it accounts for about 11 million deaths—20% of all deaths per year.
And it doesn’t just affect adults. In 2020, 2.4 million newborn babies died of sepsis in the first month of their lives. Most of these deaths happened in sub-Saharan Africa.
The main treatment for sepsis is antibiotics. However, the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in human medicine and agriculture has led to antimicrobial resistance—a process in which bacteria, fungi and parasites have developed the ability to resist the action of medicines.
The World Health Organization describes antimicrobial resistance as one of the top global public health and development threats.
This growing resistance is due to the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in both human medicine and in farming. They’re used in large quantities to grow crops and in animal feeds to treat and reduce the risk of infection in livestock.
It has been forecast that, by 2050, more people will die from antimicrobial resistance than both cancer and diabetes combined.
Sub-Saharan Africa is one of the regions with the highest rates of deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance (including sepsis) in the world, with 23.5 deaths per 100,000 people.
In our latest study we found that samples taken from mothers and newborn babies younger than one week in Nigeria already had colistin-resistant bacteria present in their bodies. But neither the babies nor their mothers had been treated with colistin.
Colistin is one of the last remaining antibiotics that is still effective in killing bacteria and fighting infections such as pneumonia. It is deemed critically important for human medicine by the World Health Organization.
We surmise that mothers may have picked up these colistin resistant bacteria from the environment. We cannot speculate on the specific mechanism. The babies, meanwhile, could have picked up the bacteria from the hospital, the community, or from their mothers. It’s not yet known if these colistin-resistant bacteria stay in the mothers or babies—but if they do this may increase their chances of acquiring future drug-resistant infections.
How we did our study
The samples from newborn babies and their mothers in our study were collected between 2015 and 2017 from three hospitals in Kano and Abuja. This research is the largest ever screening of intestinal microbiota for colistin resistance in Nigeria.
Of the 4,907 samples we analyzed in our Cardiff and Oxford laboratories, we found that 1% of samples had genes conferring colistin resistance, across 41 mothers and eight babies. Although this is a low percentage, it is extremely worrying that any babies were carrying colistin-resistant bacteria within their first week of life.
Colistin is rarely used in hospitals and clinics in Nigeria. Therefore, our findings suggest that resistance may have emerged from the increasing use of colistin in agricultural settings in the country. We are continuing our research with collaborators in Nigeria to further understand the levels of resistance in both the health care system and more broadly.
Dangers of using antibiotics in agriculture
Globally, more antibiotics are prescribed to animals than to humans. Most of this consumption is not to treat infections; rather, it is to prevent infections or promote faster growth in animals.
In 2016 mobile colistin (mcr) genes were discovered in E. coli bacteria from a pig farm in China. These genes carry resistance to the antibiotic colistin, and can spread between bacteria, furthering colistin resistance.
This discovery led to a total ban on colistin’s agricultural use in China.
In February 2022, European laws were expanded to make it illegal to add antibiotics to livestock feeds as a precaution to prevent infections before they start.
However, in a study we published in 2023, we found that, while European countries have banned the use of colistin in farming, paradoxically they still actively export livestock feeds that contain colistin to low- and middle-income countries such as Nigeria for agriculture use.
It seems a highly questionable practice to knowingly profit by selling feedstuffs banned for use in Europe to developing countries that lack these regulations—particularly when these countries already suffer from some of the highest rates globally of endemic antimicrobial resistance for common antibiotics and treatment alternatives are either prohibitively expensive or completely inaccessible.
Estimates suggest that globally almost 100,000 tons of antibiotics were used to raise cattle, sheep, chickens, and pigs in 2022. This usage is expected to increase by another 8%by 2030 and will lead to a direct increase in antibiotic-resistant infections.
Call for a total ban
There needs to be a global ban on colistin’s indiscriminate agricultural use to preserve this crucial antibiotic for when it is urgently required.
However, this is a delicate balance. A ban without alternative solutions will likely affect food production and adversely affect farmers’ livelihoods in already challenging climates. And, with the world’s population set to increase by about 2 billion by 2050, demand for affordable meat will only rise.
Urgent investment is also needed in hospital infection prevention and control programs and improved water, sanitation and hygiene facilities in farms to help to limit the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria around these environments.
Animals should be given antibiotics only when they are sick. These antibiotics should be selected from those the World Health Organization has listed as being “least important” to human health rather than from those classified as “highest priority/critically important.”
In September 2024, during the UN General Assembly in New York, leaders from governments, industry, financial institutionsand scientific organizations will come together for a UN High-Level meeting on antimicrobial resistance.
This meeting offers a timely opportunity for global leaders to set some targets to reduce antibiotic use in farming and support farmers in low- and middle-income countries to improve farm hygiene practices.
News
Babangida’s Book is filled with distorted facts, collection of lies, says Dele Farotimi

By Kayode Sanni-Arewa
Dele Farotimi, a human rights lawyer, has launched a heavy attack on former dictator Gen. Ibrahim Babangida (retd.), describing his reign as “ruinous”.
Farotimi, who lived through Babangida’s rule, recounted his experiences as a participant in the fight against the former leader’s “evil actions and inactions
Farotimi’s comments come after Babangida’s recent admission that Chief M.K.O. Abiola won the 1993 presidential election, which Babangida annulled.
The human rights lawyer expressed his disappointment, but not surprise, at the “mixed bag of lies, half-truths, urban legends, and obfuscations” in Babangida’s recent statements.
Farotimi’s criticism is not isolated, as many Nigerians have questioned Babangida’s legacy and the lack of consequences for his actions. The annulment of the 1993 election led to widespread protests and a prolonged struggle for democracy in Nigeria.
In a statement, Farotimi concluded, “No hagiographic allocutus can redeem the Evil Genius of Minna”.
The statement was shared on X while he was reacting to a comment made by Adnan Abdullahi Adam, which stated that “it’s better to read every side of exposition before forming your own judgement”.
With the cover picture of the IBB’s memoir “A Journey In Service” @realadnantweet wrote:
“I think IBB’s memoir: “A Journey in Service” exposes a fresh perspective on everything.
“It’s better to read every side of exposition before forming your own judgement.
“Everyone should try reading the book as jury to the plea of the accused.”
Responding Farotimi wrote: “I lived through his ruinous reign. I wasn’t a passive victim of his evil actions and inactions, I was a participant in the fight to be freed of him.
“I am painfully aware of the extent of his evil capabilities, and I have not been disappointed by the mixed bag of lies, half truths, urban legends, and obfuscations contained in the excerpts already in the public domain. No hagiographic allocutus can redeem the Evil Genius of Minna.”
On Thursday, February 20, 2025, former Nigerian military ruler General Ibrahim Badamasi Babangida (IBB) released his long-anticipated autobiography, “A Journey in Service.”
The memoir has ignited a firestorm of controversy, with critics accusing Babangida of distorting historical events and maligning deceased individuals who cannot defend themselves.
This development has reopened debates about his tenure and its lasting impact on Nigeria’s political and economic landscape.
Babangida’s tenure from 1985 to 1993 was marked by the implementation of the Structural Adjustment Programme (SAP), among others. In “A Journey in Service,” he provides an insider’s perspective on the adoption of SAP, aiming to offer context for the controversial policy that aimed to liberalize Nigeria’s economy.
While intended to address economic challenges, SAP led to widespread protests and debates due to its harsh austerity measures and the social hardships it imposed.
Critics, however, contend that Babangida’s memoir serves as a self-exoneration tool, selectively presenting events to absolve himself of blame.
Human rights lawyer and former Chairman of the Nigerian Human Rights Commission, Prof. Chidi Odinkalu, described the book as a “pack of lies,” accusing Babangida of making allegations against deceased individuals who cannot contest his claims.
Odinkalu further criticized Babangida for portraying himself as a victim of circumstances orchestrated by those who are no longer alive to defend themselves.
The memoir has also rekindled discussions about Babangida’s annulment of the June 12, 1993, presidential election, widely regarded as one of Nigeria’s freest and fairest elections. In the book, Babangida attempts to justify the annulment, a move that plunged the nation into political turmoil and prolonged military rule. Many Nigerians view this action as a significant setback to the country’s democratic progress.
News
Saudi Arabia plans to invest $600bn in new US trade over 4 years

By Kayode Sanni-Arewa
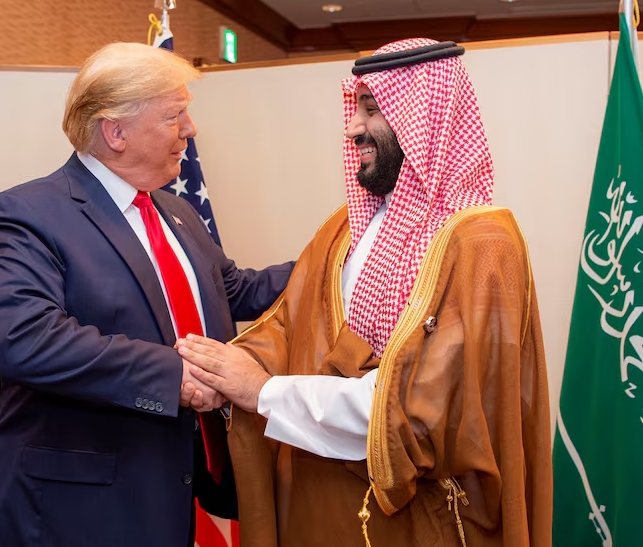
Saudi Arabian Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman told President Donald Trump that the kingdom wants to put $600 billion into expanded investment and trade with the United States over the next four years, the Saudi State news agency said early on Thursday.
In a phone call between the two leaders, the crown prince said the Trump administration’s expected reforms could create “unprecedented economic prosperity”, the state news agency reported.
The report said Saudi Arabia wants its investments to capitalize on these conditions. It did not detail the source of the $600 billion, whether it would be public or private spending nor how the money would be deployed.
The investment “could increase further if additional opportunities arise”, the agency quoted Bin Salman as telling Trump.
Trump fostered close ties with Gulf states including Saudi Arabia during his first term. The country invested $2 billion in a firm formed by Jared Kushner, Trump’s son-in-law and former aide, after Trump left office.
Trump said following his inauguration on Monday that he would consider making Saudi Arabia his first destination for a foreign visit if Riyadh agreed to buy $500 billion worth of American products, similar to what he did in his first term.
“I did it with Saudi Arabia last time because they agreed to buy $450 billion worth of our product. I said I’ll do it but you have to buy American product, and they agreed to do that,” Trump said, referring to his 2017 visit to the Gulf kingdom.
The Reuters Daily Briefing newsletter provides all the news you need to start your day. Sign up here.
Reporting by Hatem Maher; Editing by Leslie Adler and Cynthia Osterman
News
NDPC Finally Secures NJI’s Support for Data Privacy Right in Nigeria

By Kayode Sanni-Arewa
The Nigeria Data Protection Commission (NDPC) has secured the support of the National Judicial Institute (NJI)
. It will be recalled that the NJI is responsible for the training of judicial officers in Nigeria from magistrate courts to the Supreme Court of Nigeria.
During a courtesy visit of the Commission, to NJI, the National Commissioner and CEO of the NDPC, Dr Vincent Olatunji lauded the management of NJI under the leadership of Hon. Justice Salisu Garba Abdullahi, (Rtd) for the milestones the Institute has achieved in human capital development particularly in relation to judicial officers and fellows of the institute.
While commenting on the importance of the Nigeria Data Protection Act in the face of disruptive technologies, Dr. Olatunji reiterated the need to collaborate with NJI in keeping judicial officers abbrest of privacy Jurisprudence.
He noted that decisions on enjoyment of data privacy rights in relation to one citizen have fundamental implications on all citizens.
“It is the digital age, and the protection of the privacy of all citizens worldwide is paramount. It is now the right of all citizens to have their privacy protected. This is why countries across the globe are putting adequate measures in place to ensure enforceable data protection rights, as well as establishing data protection authorities to enforce data protection laws,” Dr Olatunji stated.
In his response, Hon Justice Abdullahi commended the NDPC, under Dr Olatunji’s leadership, for its significant achievements since its establishment. He pledged to collaborate with the NDPC to raise awareness on data protection and privacy within the judiciary and accepted the NDPC’s proposal anchored on capacity building for judges, NJI fellows, and employees.
According to the eminent jurist “The issue of data protection is very important. It is new, and judges need to be trained. The first step we should take is to review the Act (NDP Act) that established the Commission. Additionally, there is a need for us to train our fellows on data protection.”
NJI and NPC have put in place a technical working group that will draw up a work plan and coordinate the initiatives for capacity building. The working group is expected to report back within days in order to commence implementation.



-

 News22 hours ago
News22 hours agoJust in : Senator Gumau is dead
-

 News23 hours ago
News23 hours ago10th NASS Committed to Constitutional Reforms – Kalu
-

 Metro15 hours ago
Metro15 hours agoInsecurity! Gunmen invade church, slash pastor’s 2 fingers
-

 News22 hours ago
News22 hours agoRep Salam Congratulates Governor Adeleke On Successful Conduct Of LG Elections
-

 Metro15 hours ago
Metro15 hours agoFire engulfs MTN office in Oyo
-

 News21 hours ago
News21 hours agoPolice seal OSSIEC office, officials nabbed, says chairman
-

 News21 hours ago
News21 hours agoI have never insulted President Tinubu in my entire life”-Gov Adeleke
-

 Foreign14 hours ago
Foreign14 hours agoPentagon set to sack 5400 staff as attack hits Trump’s downsizing plan







