Economy
CBN names Gidado Polaris Bank board chair
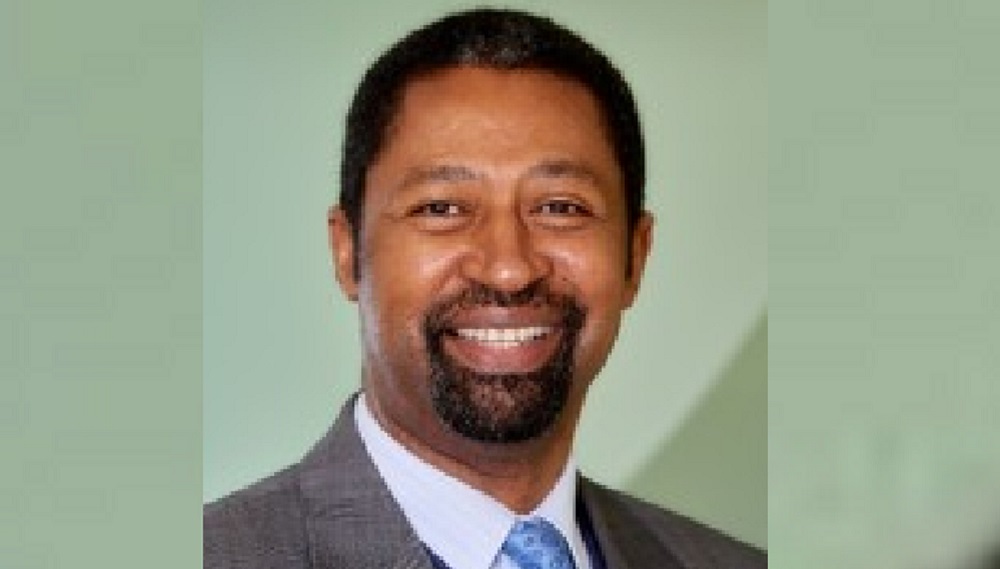

The Central Bank of Nigeria has announced the appointment of the members of the board of directors for Polaris Bank.
In a statement on Monday, the bank disclosed that Kassim Gidado was appointed as the board chairman.
The new Polaris Bank board is the chief of staff at MAG Group Limited and advisor to various governments.
Also, Akwa Okon, with a background in law and finance, was named a non-executive director.
He previously served as managing director of the Niger Delta Development Commission and is a chartered accountant.
Other non-executive directors of the bank are Mallam Umar; Ayaba Ayo-Joseph; Giwa-Amu Ibironke, and Onosode Christopher.
The Managing Director/Chief Executive Officer of Polaris Bank, Kayode Lawal, welcomed the new board members, describing the appointments as a step towards achieving growth and value for stakeholders.
In January, the CBN dissolved the boards and managements of Union Bank of Nigeria, Keystone Bank and Polaris Bank over alleged corporate governance infractions and non-compliance with regulatory requirements.
This came barely three weeks after the Special Investigator on the CBN and Related Entities, Jim Obazee, submitted its final report to President Bola Tinubu.
In a statement by the acting Director of Corporate Communications, CBN, Sidi Hakama, the central bank said the affected banks’ alleged infractions varied from regulatory non-compliance, corporate governance failure, disregarding of the conditions under which their licences were granted, and involvement in activities that posed a threat to financial stability, among others.
Recall that the apex revoked the operating license of Skye Bank on September 21, 2018, and renamed it Polaris Bank.
The then CBN Governor, Godwin Emefiele, said AMCON would take over all the assets and liabilities of the defunct entity.
Economy
75.5% of rural Nigerians now live below poverty line — World Bank

The World Bank has disclosed that a staggering 75.5 per cent of rural Nigerians are now living below the poverty line, reflecting deepening hardship in the country’s hinterlands.
This was revealed in the Bank’s April 2025 Poverty and Equity Brief for Nigeria, which paints a grim picture of worsening economic hardship, widening inequality, and persistent underdevelopment across much of the nation.
While poverty is widespread among urban populations, the report emphasised that the situation is significantly worse in rural areas, where economic stagnation, high inflation, and insecurity have exacerbated living conditions.
“Based on the most recent official household survey data from Nigeria’s National Bureau of Statistics, 30.9 per cent of Nigerians lived below the international extreme poverty line of $2.15 per person per day in 2018/19 before the COVID-19 pandemic,” the report stated.
The report also highlighted Nigeria’s enduring regional disparities. “Nigeria remains spatially unequal. The poverty rate in northern geopolitical zones was 46.5 per cent in 2018/19, compared with 13.5 per cent for southern ones. Inequality measured by the Gini index was estimated at 35.1 in 2018/19.
“Nigeria’s Prosperity Gap — the average factor by which individuals’ incomes must be multiplied to attain a prosperity standard of $25 per day for all — is estimated at 10.2, higher than most peers.”
Despite successive policy interventions, these figures underscore a persistent economic divide across the country.
The report’s demographic analysis found that children aged 0 to 14 years had a poverty rate of 72.5 per cent, reflecting the scale of deprivation among the youngest segment of the population.
Gender disparities were also observed, with 63.9 per cent of females and 63.1 per cent of males classified as poor under the $3.65 per day lower-middle-income threshold.
Education emerged as a significant determinant of poverty, with Nigerians lacking formal education experiencing a poverty rate of 79.5 per cent. This contrasts with 61.9 per cent for those with primary education and 50.0 per cent for secondary school graduates. Only 25.4 per cent of those with tertiary education were considered poor.
The report also drew attention to multidimensional poverty indicators, which further reflect widespread deprivation.
According to the World Bank, about 30.9 per cent of Nigerians live on less than $2.15 daily, 32.6 per cent lack access to limited-standard drinking water, 45.1 per cent do not have limited-standard sanitation, and 39.4 per cent have no electricity.
Education access remains a challenge, with 17.6 per cent of adults yet to complete primary education, and 9.0 per cent of households reporting at least one school-aged child not enrolled in school.
The report noted that even before the COVID-19 pandemic, efforts to reduce extreme poverty had largely stalled.
“Before COVID-19, extreme poverty reduction had almost stagnated, dropping by only half a percentage point annually since 2010. Living standards of the urban poor are hardly improving, and jobs that would allow households to escape poverty are lacking,” the report read.
Although the World Bank acknowledged recent economic reforms aimed at stabilising Nigeria’s macroeconomic outlook, it warned that persistently high inflation continues to undermine household purchasing power, particularly in urban areas where incomes have not kept pace with rising costs.
In light of the worsening situation, the Bank called for urgent policy action to shield vulnerable groups from inflationary shocks and to drive job creation through more productive economic activities.
Economy
Naira Records Marginal Decline Against Dollar at Official Market

The Nigerian naira experienced a mild drop in value on Friday, closing at ₦1,602.18 per dollar in the official foreign exchange market, based on figures released by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN).
This marks a decrease of ₦5.49 from the rate of ₦1,596.69 recorded on April 30, the last trading day before the May 1 Workers’ Day holiday—indicating a depreciation of approximately 0.34%.
Earlier in the week, from Monday to Wednesday, the naira remained relatively stable, exchanging at ₦1,599.95, ₦1,599.71, and ₦1,596.69 respectively.
Although the local currency showed some consistency mid-week, it wrapped up the week with a loss, following a sligh dip of 0.02% at the beginning of the week
Economy
Black Market Dollar hits N1,610 Amid Economic quagmire

What is the Dollar to Naira Exchange Rate in the Black Market (Also Known as the Parallel Market or Aboki FX)?
Below is the black market exchange rate for the U.S. dollar to the Nigerian naira as of Thursday, May 1, 2025. These are the typical rates at which you can exchange dollars for naira:
Dollar to Naira Black Market Exchange Rate (May 1, 2025):
At the Lagos Parallel Market, also referred to as the black market, Bureau De Change (BDC) operators are buying dollars at ₦1,602 and selling at ₦1,610, according to market sources.
Please note: The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) does not recognize or endorse transactions conducted on the parallel market. The CBN advises individuals and businesses seeking foreign exchange to use official banking channels.
-

 News23 hours ago
News23 hours agoFive Asian countries Nigerians can visit without a visa
-

 Entertainment24 hours ago
Entertainment24 hours agoOld Prophecy Of Pastor About VeryDarkman Goes Viral After His Arrest
-
 News23 hours ago
News23 hours agoInsecurity! Bandits abduct 25 female wedding guests
-

 News23 hours ago
News23 hours agoTompolo Launches Door-to-Door Campaign for Tinubu’s 2027 Re-Election!
-

 News23 hours ago
News23 hours agoEzekwesili slams political establishment over harassment allegation, defends Natasha
-

 News11 hours ago
News11 hours agoFormer Plateau deputy governor is dead
-

 News17 hours ago
News17 hours agoINTERPOL uncovers 150 stolen vehicles from Canada in Nigeria, Gambia, other W.A. countries
-

 News23 hours ago
News23 hours agoKyari breaks silence: “I’m not in EFCC custody, I served God, country, not corruption”






