Health
‘Blessed’: US Woman Sees Second Chance In Life After Pig Kidney Transplant
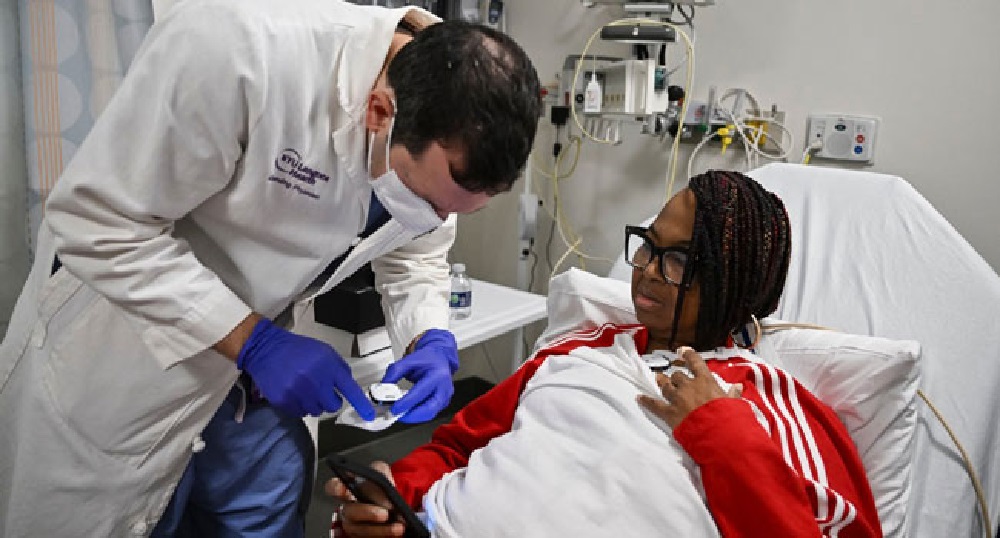
Towana Looney donated a kidney to her mother in 1999 only for the remaining one to fail years later due to pregnancy complications.
Now, the 53-year-old from Alabama has become the latest recipient of a gene-edited pig kidney — and is currently the only living person in the world with an animal organ transplant, New York’s NYU Langone hospital announced Tuesday.
“I’m overjoyed, I’m blessed to have received this gift, this second chance at life,” Looney said during a press conference, held three weeks after the procedure.
Xenotransplantation, transplanting organs from one species to another, has long been a tantalizing yet elusive scientific goal. Early experiments on primates faltered, but recent advances in gene editing and immune system management have brought the dream closer to reality.
Pigs have emerged as the ideal donors: they grow quickly, produce large litters and are already part of the human food supply.
Advocates hope this approach can help address the severe organ shortage in the United States, where more than 100,000 people are waiting for transplants, including over 90,000 in need of kidneys.
A last chance
Looney had been living with dialysis since December 2016 — eight grueling years. High blood pressure caused by preeclampsia had taken its toll, leaving her with chronic kidney disease.
Despite receiving priority on transplant waiting lists as a living donor, her search for a compatible kidney was a frustrating dead end. Her unusually high levels of harmful antibodies made rejection almost inevitable, and as her body lost viable blood vessels to support dialysis, her health declined.
Out of options, Looney applied to join a clinical trial for pig kidney transplants, and finally underwent the seven-hour surgery on November 25.
Asked how she felt afterward, Looney’s joy was infectious. “I’m full of energy, I’ve got an appetite… and of course, I can go to the bathroom. I haven’t been going in eight years!” she laughed, adding that she plans to celebrate at Disney World.
Jayme Locke, a surgeon on the transplant team, described the results with awe. “The kidney functioned essentially exactly like a kidney from a living donor,” she said, adding that Looney’s husband saw a rosiness in her cheeks for the first time in years.
“That is the miracle of transplantation.”
Cautious optimism
Looney’s surgery is the third time a gene-edited pig kidney has been transplanted into a human who is not brain dead.
Rick Slayman, the first recipient, died in May, two months after his procedure at Massachusetts General Hospital. The second, Lisa Pisano, initially showed signs of recovery following her surgery at NYU Langone, but the organ had to be removed after 47 days, and she passed away in July.
Looney, however, was not terminally ill before the transplant, noted Robert Montgomery, who led the surgery. Each case, he emphasized, provides critical lessons for refining the techniques.
The kidney was provided by biotech company Revivicor, which breeds genetically modified herds in Virginia. A Massachusetts-based company, eGenesis, provided the kidney for Slayman.
Looney’s organ has 10 genetic edits to improve compatibility with the human body — an advance over Revivicor’s earlier efforts that used kidneys with a single gene edit and included the pig’s thymus gland to help train the host’s immune system and prevent rejection.
Montgomery, a pioneer in the field who performed the world’s first gene-edited pig organ transplant in a brain-dead patient in 2021, said both methods are likely to enter clinical trials “probably by this time next year, or even sooner.”
“This is a watershed moment for the future of transplantation,” said Kevin Longino, CEO of the National Kidney Foundation. The nonprofit’s polling shows that patients and families favor faster clinical trial progress, believing the risk of inaction outweighs the uncertainties of xenotransplantation.
Looney was discharged December 6 to a nearby New York City apartment. Though her high antibody levels remain a concern, doctors are monitoring her closely using wearable technology and are trying a novel drug regimen to prevent rejection.
Periodic hospital visits may still be required, but the team remains optimistic she can return home in three months.
AFP
Health
SAD! Lassa Fever Claims 127 Lives Across 18 States in Nigeria(List)

The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) has reported a sharp rise in Lassa fever cases, with 127 deaths confirmed across 18 states as of April 6, 2025.
According to the agency’s latest situation report, 674 people have tested positive for the virus out of 4,025 suspected cases recorded between January and early April.
The current Case Fatality Rate (CFR) stands at 18.8%, slightly higher than the 18.5% recorded during the same period in 2024, indicating a worrying upward trend.
The most affected states include Taraba (31 deaths), Ondo (26), Edo (17), Bauchi (12), and Ebonyi (11). Other states with reported fatalities are Gombe (7), Kogi (4), Benue (4), Nasarawa (4), Plateau (5), Kaduna (2), and one death each in Enugu, Delta, Cross River, and Ogun.
The report also highlights that 71% of confirmed cases were concentrated in Ondo (30%), Bauchi (25%), and Edo (16%), with the remaining 29% spread across 15 other states. The virus has now reached 93 local government areas nationwide.
Lassa fever is a viral haemorrhagic illness transmitted mainly through exposure to food or household items contaminated by infected rodents, particularly the multimammate rat. It can also spread through direct contact with the blood, urine, feces, or other bodily secretions of an infected person.
The disease predominantly affects people between the ages of 21 and 30, with a male-to-female ratio of 1:0.8, according to NCDC data.
In response to the outbreak, the NCDC has activated the National Lassa Fever Multi-Partner, Multi-sectoral Incident Management System to strengthen surveillance, case management, risk communication, and coordination efforts at all levels.
As the country continues to battle the spread of the virus, the NCDC is urging citizens to maintain proper hygiene, store food in rodent-proof containers, and seek immediate medical attention if symptoms such as fever, headache, sore throat, chest pain, or vomiting occur
Health
FG identifies 1,277 persons for monitoring as Lassa fever kills 122
The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention has listed 1,277 persons for follow-up over the possibility of being infected with Lassa fever. This follows the centre recording 659 confirmed cases out of 3,779 suspected cases and 122 deaths in 13 weeks (from January to March 30, 2025).
A report obtained from the NCDC on Friday indicated that no fewer than 18 states across the country have recorded Lassa fever cases, with Ondo, Bauchi, and Edo being the most affected.
The report partly reads, “Cumulatively, in week 13 of 2025, 122 deaths have been reported, with a Case Fatality Rate of 18.5%, which is lower than the CFR for the same period in 2024 (18.7%).
“In total for 2025, 18 states have recorded at least one confirmed case across 93 Local Government Areas. Seventy-one per cent of all confirmed Lassa fever cases were reported from these three states (Ondo, Bauchi, and Edo), while 29% were reported from 15 other states with confirmed Lassa fever cases. Of the 71% of confirmed cases, Ondo reported 30%, Bauchi 25%, and Edo 16%.
“The predominant age group affected is 21-30 years (Range: 1 to 94 years, Median Age: 30 years). The male-to-female ratio for confirmed cases is 1:0.8. The number of suspected cases increased compared to that reported for the same period in 2024. No new healthcare worker was affected in week 13. The National Lassa fever multi-partner, multi-sectoral Incident Management System (IMS) was activated to coordinate the response activities at all levels.”
The report shows that the contacts under follow-up number 1,277, while the contacts that have completed follow-up total 1,448.
According to the NCDC, the disease has affected 20 healthcare workers in eight states so far this year.
Lassa fever is an acute viral haemorrhagic fever caused by the Lassa virus. The natural reservoir for the virus is the multimammate rat (also known as the African rat), although other rodents can also act as carriers.
The public health institute stated that Lassa fever cases occur year-round, with peak transmission periods typically from October to May.
Health
WHO calls for countries to address disruptions to TB services
In the wake of massive cuts in US funding, the World Health Organization (WHO) today called on global health leaders, donors, and policymakers to protect and maintain tuberculosis (TB) care and support services around the world.
In a statement issued ahead of World Tuberculosis Day (March 24), the WHO said the “drastic and abrupt” cuts to global health funding threaten to reverse gains made in global efforts to combat TB, which remains the world’s deadliest infectious disease. Those efforts have saved an estimated 79 million lives worldwide since 2000, the organization said.
“The huge gains the world has made against TB over the past 20 years are now at risk as cuts to funding start to disrupt access to services for prevention, screening, and treatment for people with TB,” said WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD. “But we cannot give up on the concrete commitments that world leaders made at the UN General Assembly just 18 months ago to accelerate work to end TB. WHO is committed to working with all donors, partners and affected countries to mitigate the impact of funding cuts and find innovative solutions.”
USAID cuts have crippled TB control efforts
While the statement does not specifically mention the US Agency for International Development (USAID), the Trump administration’s freeze of USAID funding, and the subsequent canceling of thousands of contracts issued by the agency, have left a gaping hole in funding for TB prevention, screening, and treatment services. The US government has been the leading bilateral donor to global TB control efforts, contributing $200 million to $250 million annually—roughly one quarter of international donor funding for the disease.
The WHO said 27 countries are facing crippling breakdowns in their TB response, with the biggest impact seen in high-TB burden countries in Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Western Pacific. Among the services that have been disrupted are diagnosis, active case finding, screening, and contact tracing, and those disruptions are resulting in delayed detection and treatment and increased transmission risk. Drug supply chains, laboratory services, and data and surveillance systems have also been undermined.
A recent update from StopTB Partnership, which works on TB response with more than 2,000 partners in 100 countries, provides some detail on the services affected by the USAID funding cuts. In Cambodia, active case finding has halted in half the country, resulting in 100,000 people missing TB screening and 10,000 cases of drug-susceptible (DS)-TB going undetected. In Kenya, sputum sample transport once supported by USAID has halted, affecting the diagnosis of DS- and drug-resistant (DR)-TB. In India, USAID-funded TB screening projects in vulnerable groups have stopped.
The huge gains the world has made against TB over the past 20 years are now at risk as cuts to funding start to disrupt access to services for prevention, screening, and treatment for people with TB.
Those are just three of dozens of examples. In a news release today, StopTB Partnership Executive Director Lucica Ditiu, MD, echoed Tedros’s call for action.
“People with TB need us,” Ditiu said. “We have to remain strong, and we can never ever give up the fight. Through innovative, global and national efforts and standing together, we will be able to achieve these targets of ensuring TB prevention, treatment, and care are accessible to all.”
TB was responsible for an estimated 1.25 million deaths in 2023, according to the WHO’s most recent annual report. An estimated 8.2 million people were newly diagnosed with the disease—the most cases in a year recorded by the WHO since it began global TB monitoring in 1995. High-burden TB countries have only recently begun to recover from the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, which the WHO estimates resulted in 700,000 excess TB deaths.
Cuts exacerbate funding shortfalls
As the WHO notes, the funding cuts come amid what was already a shortfall in funding for global TB control efforts. In 2023, $5.7 billion was available for TB prevention, diagnostic, and treatment services in low- and middle-income countries, but that’s only 26% of the 2027 target goal of $22 billion. TB research is receiving just one fifth of its 2022 target of $5 billion. Cuts to US funding are only going to exacerbate the problem.
In a joint statement issued earlier this week, Tedros and the Civil Society Task Force on Tuberculosis called on countries to take urgent action to prevent any disruption to TB services, ensure domestic resources to sustain equitable and essential TB care, and safeguard essential TB drugs, diagnostics, care, and social protection coverage for TB patients. They also urged the establishment of national partner platforms that would bring together public and private sectors, civil society, nongovernmental organizations, professional societies, and donors to maintain momentum against TB in affected countries.
“This urgent call is timely and underscores the necessity of swift, decisive action to sustain global TB progress and prevent setbacks that could cost lives,” said Tereza Kasaeva, PhD, director of WHO’s Global Programme on TB and Lung Health, in today’s WHO news release.
-

 News12 hours ago
News12 hours agoDSS arrests Army major for planning unrest in Delta
-

 News12 hours ago
News12 hours agoFCT minister, Wike announces new appointments
-

 Politics13 hours ago
Politics13 hours agoSee list of APC Delta stakeholders holding meeting in Abuja on power sharing formula with Oborevwori
-

 News13 hours ago
News13 hours agoCOVID-19 Vaccine Killed Pope Francis, says Pastor Oyakhilome
-

 News6 hours ago
News6 hours agoNDLEA storms Lagos hotel, recovers N1.042billion illicit drug consignments(Photos)
-

 News13 hours ago
News13 hours agoUK Tories mull replacing Badenoch as party leader after poor ratings
-

 News13 hours ago
News13 hours agoOborevwori absent as Delta APC leaders meet with Uzodinma in Abuja
-

 News12 hours ago
News12 hours agoEquities Investors Lose N202bn as Dangote Cement Undergoes Reversal