News
Why Price Of Food Won’t Drop Immediately Despite Naira Appreciation

As the Nigerian naira experiences an upturn against the dollar, economists have indicated that the positive effects on the country’s commodity prices might not be immediate.
Speaking to Punch, CEO of Economic Associates, Ayo Teriba, highlighted the time lag in the impact of currency fluctuations on market prices.
According to Teriba, while the strengthening naira is a positive sign for the economy, the translation of this development into reduced commodity prices will not be instantaneous.
Consumers may have to wait before seeing a noticeable decrease in the cost of goods and services, as market dynamics and pricing mechanisms gradually adjust to the new exchange rate reality.
He noted, “Foods that have been bought at the old exchange rate will still be tied to the old exchange rate.
“Whether a month or a quarter, it depends on the duration it takes to order and sell. The effect we should hope to see is that the prices have stopped going up. We call it acceleration.”
Echoing similar sentiments, President of Nigerian Economic Society, Adeola Adenikinju, highlighted the economic rationale behind the delay in price adjustments.
Adenikinju stated, “What people have in stock now was purchased at high prices. If they sell at lower prices, they are going to record losses.
“So until they replace the current one, that is when they will reduce their prices.
“But currently, to avoid losses, they will still sell at the rate at which they bought it. We will only start seeing the current prices of things as current stock is sold and new stock is acquired.”
According to Adenikinju, the central bank’s actions in the next few weeks will also reflect what the sellers will do.
He said, “They will be watching the markets to see if CBN will be able to sustain the stability of the naira.”
Nigeria has been battling soaring inflation, which accelerated to 31.70 per cent in February from 29.90 per cent in the previous month, driven primarily by food inflation, which rose to 37.92 per cent.
To tame the pacing inflation, the CBN raised the benchmark interest rate to 22.75 per cent in February from 18.75 per cent and further reviewed it upward to 24.75 per cent on Tuesday.
According to Professor of Economics, Babcock University, Onakoya Adegbei, the fact that prices go up and never come down is not peculiar to Nigeria.
He said, “Reduction in production usually comes with a lag because of rigidity in production.”
He emphasised that market expectations usually drive the delay.
“There is usually a lag and that is due to the expectation theorem. For example, if you expect the price of rice to increase, you will buy more and keep it in the house, So, it will increase your demand. But if you expect that prices will fall, what you already have you cannot dispose of.
“Reduction in production usually comes with a lag because of rigidity in production. If you already produce a certain product at a certain price and the price in the market is falling, you will then wait to see if the reduction will be sustainable. If you see that it is sustainable, then you can make a move to reduce the prices of your product. It is a lag effect,” Adegbei explained.
A foodstuff seller at EFAB market, Favour Uche told the platform, “The price of rice didn’t reduce even now that the dollar is down.”
Uche emphasised the challenges faced by traders, including the expenses incurred to maintain product quality amid infrastructural constraints.
“The price of rice didn’t decrease. Even now that the dollar is down, it still hasn’t reduced. For example, a carton of Titus fish cost N90,000 two weeks ago but today, the same carton of fish is sold at N95,000 as of March 29, 2024.
“Even with the fact that the dollar has reduced, but being in the system, I think I understand why. It is because they use one-third of their profit to buy diesel to cool these fish and keep them frozen. After all, there is no light. So, I understand their pain and why the prices are like that,” she added.
Another trader, Abdul Yusuf, who sells meat, asserted, “Price did not come down even with the dollar fall.
“Two weeks ago the price of one kilogramme of meat was selling at N4,800 but now, it is N5,000. So, the price did not come down even with the dollar falling.”
News
TETFUND threatens to cut financial support to non-performing institutions

The Tertiary Education Trust Fund (TETFUND) has threatened to cut financial support to beneficiary tertiary institutions that fail to meet performance benchmarks or mismanage allocated funds.
The agency said it would de-list such tertiary institutions from its support programmes.
Executive Secretary of TETFUND, Sonny Echono gave the warning at a one-day strategic engagement with heads of institutions, bursars, and heads of procurement of the agency’s beneficiary institutions in Abuja on Monday.
Echono said the policy was not meant to punish, but rather safeguard the credibility and impact of TETFUND interventions.
He said: “Let me be clear, institutions that consistently fail to access, utilise or retire funds appropriately, or that fall short of enrollment and academic performance thresholds, risk being delisted as TETFUND beneficiary institutions.”
He also disclosed the intention of TETFUND to ensure that its resources were directed towards institutions that were committed to high standards of governance, transparency, and accountability.
Echono said the strategic engagement was targeted at addressing recurring challenges in Nigeria’s tertiary education sector, improving project execution, and enhancing the quality of education.
A key focus, he said, was the Academic Staff Training and Development (AST&D) intervention.
He said due to rising costs and incidents of scholars absconding, the foreign component of the TETFUND Scholarship for Academic Staff (TSAS) was suspended as of January 1, 2025 with emphasis now shifted to cost-effective, locally driven training.
Echono said this year’s intervention budget prioritises consolidation, sustainability, and the completion of abandoned projects.
He added: “This engagement is not merely a meeting but a strategic convergence. It is designed to address recurring issues of concern, streamline project implementation, and enhance the overall quality of tertiary education delivery in our nation.
“As we move forward, let us approach today’s discussions with openness, collaboration, and a shared vision to elevate our institutions and the students we serve.
“Together, we can strengthen accountability, drive innovation, and ensure that the legacy of TETFUND remains impactful, equitable and enduring for generations to come.”
Executive Secretary of the National Universities Commission (NUC), Professor Abdullahi Ribadu emphasised the importance of the meeting for evaluating the implementation and impact of TETFUND – supported projects in higher education institutions.
The NUC chief, who was represented by Dr. Joshua Atah appreciated TETFUND’s vital role in improving infrastructure, research, staff development, and academic quality, stating that without its support, public education would struggle to survive.
Prof. Ribadu acknowledged the adaptability of TETFUND’s policies, such as suspending international scholarships to reallocate resources more effectively.
He urged tertiary institutions to be more responsive and ensure that interventions were relevant and efficiently executed.
Ribadu encouraged judicious and timely use of funds and called for open and constructive dialogue during the engagement.
“This calls for greater responsiveness also on the part of the institutions. This responsiveness also includes the areas of the design and implementation of these interventions to ensure that they remain relevant, impactful, and aligned with the future of education in Nigeria.
“It’s also important that we judiciously utilise these resources, and not just judicious utilisation but also in a timely manner so that we don’t lose the fund,” he said.
News
Again, Boko Haram reportedly attack military base in Borno
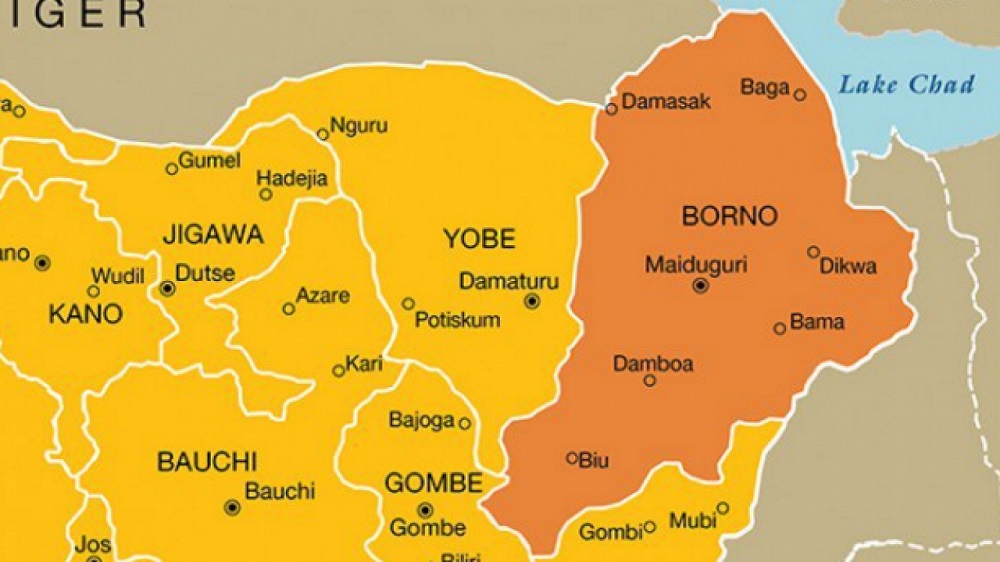
Suspected Boko Haram terrorists have attacked a Nigerian Army base in Marte , the headquarters of Marte Local Government Area of Borno State with casualties
The terrorists attacked the 153 Task Force Battalion’s Forward Operation Base (FOab) at around 3am on Monday, according to the locals and security sources.
They said the terrorists also burnt armoured tanks and seized arms and ammunition from the base during the attack.
“ISWAP has taken over Marte. An unspecified number of soldiers were killed, some captured, and many others fled towards Dikwa.
“They are currently at the 24 Task Force Brigade in Dikwa,” a source said.
Recent terrorist attacks have targeted several military formations in Borno and Yobe, including Sabon Gari and Buni Yadi, with the latest being the attack on the 153 Task Force Battalion.
Attempts to reach Maj-Gen Markus Kangye, Director of Defence Media Operations, were unsuccessful as he didn’t answer calls or respond to text messages.
News
Taraba Woos Global Investors Ahead of Landmark Economic Summit

…Taravest 2025 to Unlock Opportunities in agric, energy, mining
…as state offers peace, resources, incentives
By Gloria Ikibah
The Federal Government and Government of Taraba State have called on the international community and private sector players to partner with Taraba in unlocking the state’s massive investment potentials across agriculture, energy, mining, and tourism.
This call comes ahead of the Taraba International Investment Summit (Taravest), with the theme: “Unlocking Taraba’s Investment Potentials, Advancing Agriculture, Energy, Mining and Industrialization for sustainable development “, scheduled for May 21, 2025, in Jalingo, Taraba state.
Speaking at the diplomatic preparatory briefing in Abuja, the Minister of Foreign Affairs, Ambassador Yusuf Maitama Tuggar, who was represented by Ambassador Anderson Madubike commended the initiative, describing it as a platform that aligns with Nigeria’s economic diplomacy agenda.

“I wish to commend His Excellency and indeed the Government of Taraba State for convening this timely summit, particularly at this time when the whole world is in need of creating a travelling investment climate through co-location. There is therefore the need for partnership between governments, private sector players, and civil societies,” the Minister stated.
He emphasised that Taravest represents “a collective pursuit of development and prosperity, not only for Taraba State, but indeed for the whole world.
“They have enormous resources—we’re talking about gold, we’re talking about uranium, and many others, and of course agriculture, fertile land, which you know, food, is the way to go”, he added.
Ambassador Madubike noted that the theme for the summit, themed “Unlocking Taraba’s Investment Potentials: Advancing Agriculture, Energy, Mining, and Industrialization for Sustainable Growth,” is expected to attract both local and international stakeholders.
“Our presence here signifies a commitment to making Taraba a model of investment and sustainable development,” he said.
In his address, the Executive Governor of Taraba State, Dr. Agbu Kefas, expressed gratitude to the Federal Ministry of Foreign Affairs and extended an open invitation to diplomats and investors.
Dr. Agbu highlighted the significance of the summit as the first of its kind since the state was created in 1991, and laid out three clear objectives.
“It is my great honor to welcome you to the Paivota Preparatory Meeting for the Taraba State International Investment Summit, Taravest 2025, in just nine days to come.
“To orient you to Taraba’s untapped potentials and the structure of the summit; to inspire your confidence in our security, infrastructure, and business environment; and to enlist your support in rallying investors, technical partners, and development agencies”, the governor said.
He emphasised Taraba’s strategic strengths, citing five core advantages, this is as he reassured guests about the state’s security readiness.

“Peace and security, over 44,000 km² of fertile land for agriculture, massive hydropower and solar capacity, rich mineral reserves including gold, barite, and lithium, and growing opportunities in tourism and the digital economy.
“I want to assure you that we have coordinated with the state security services, the Nigerian military, the Nigerian police, and our traditional rulers… to guarantee your safety”, he added.
The summit, he explained, will feature B2B and B2G matchmaking, policy dialogues, PPP frameworks, and guided site visits to model farms and mining zones.
“Taravest 2025 is more than a conference. It is a statement of fact that Taraba is open for transformative partnership. I invite you to leverage your good offices to mobilize your government and business communities,so that together we will convert promise into progress and unlock a future of shared prosperity”, Dr. Agbu added.
He also urged embassies to submit the names of participating investors and delegates by May 16, 2025, to ease logistics.
Taravest 2025, which will hold at the Banquet Hall of the Government House in Jalingo, aims to attract capital, expertise, and innovation to transform Taraba into a thriving investment destination and economic powerhouse.
-

 News17 hours ago
News17 hours agoJust in: Wike admits Fubara alongside 2 govs visited him on reconciliatory moves
-

 News21 hours ago
News21 hours agoRivers crisis: Wike’s aide mocks Fubara, advises him to honourably quit since his spirit has left Brick House
-

 News14 hours ago
News14 hours agoGo home to face corruption probe, protesters in London tell Kyari (Photos)
-

 Economy19 hours ago
Economy19 hours agoSEE Black Market Dollar (USD) To Naira (NGN) Exchange Rate Today 12th May 2025
-

 News20 hours ago
News20 hours agoJapa! UK to End Overseas Care Worker Recruitment to Cut Migration
-

 News21 hours ago
News21 hours agoJust in: Chris Piwuna emerges as new ASUU President
-

 News17 hours ago
News17 hours agoAMCON, Others Dragged to Court Over Alleged Undervalued Sale of Ibadan Disco for $62m
-

 News21 hours ago
News21 hours agoEx-Senate President , Saraki chairs PDP strategy committee on way forward






